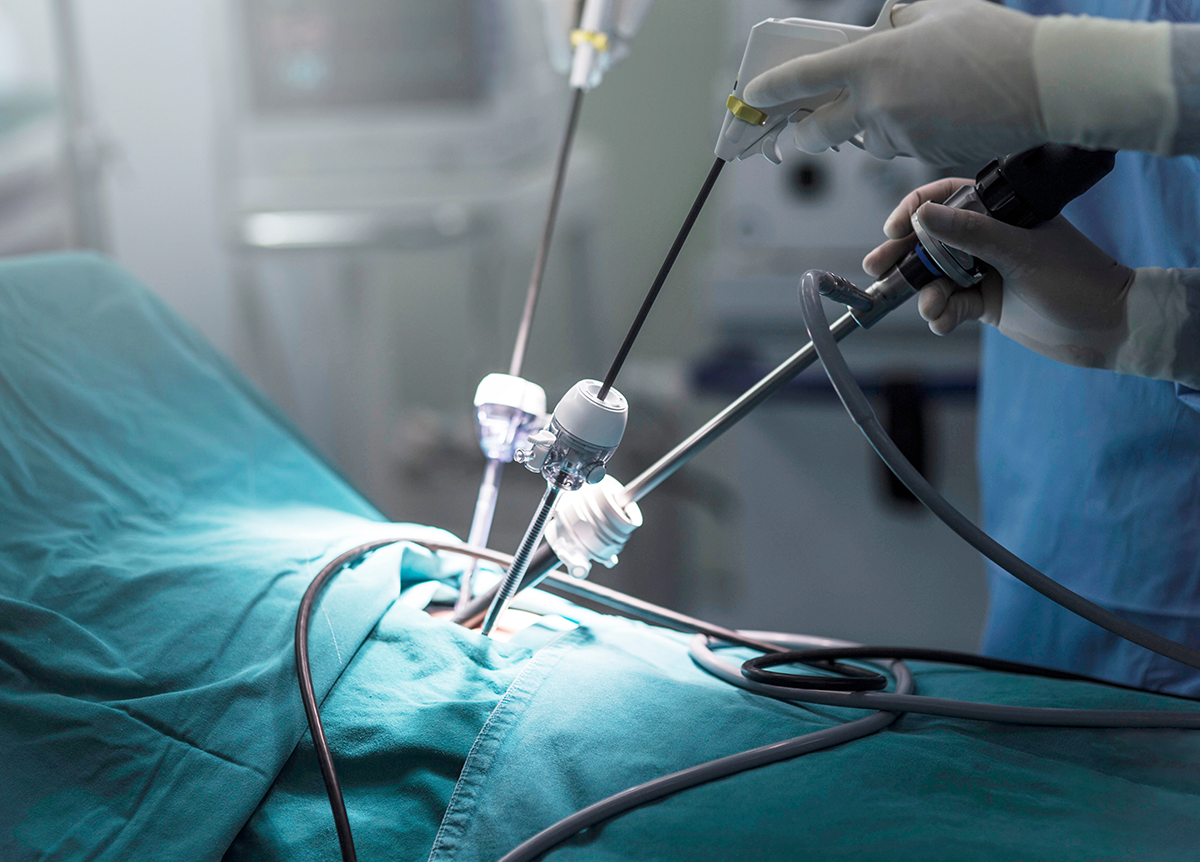
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is a successful surgical technique performed by making small incisions in the body, depending on the area where the surgery will be performed, without making large incisions like in open surgery. It is both aesthetically pleasing and functionally effective. Many surgeries in urology, obstetrics and gynecology, general surgery, and other branches can be performed using laparoscopic surgery. After the incisions are made, the body cavity is inflated with gas to create a workspace. Sterile surgical instruments are used in laparoscopic surgery, just like in open surgery. These surgeries must be performed by experienced surgeons, just like in open surgery.
The picture shows the scar marks of a patient who had laparoscopic surgery for cancer in the right kidney. In an open surgery, the incision made for this patient should have been at least 50 cm long. However, with a successful laparoscopic operation that did not exceed a total of 5 cm, the patient has recovered well.
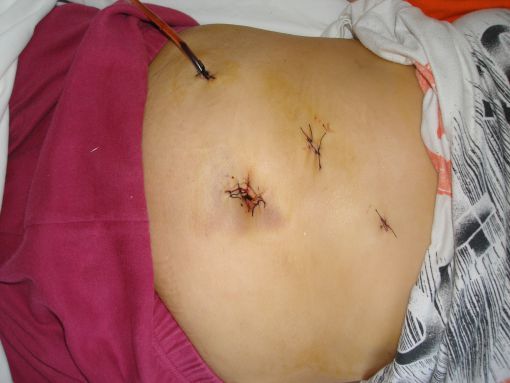
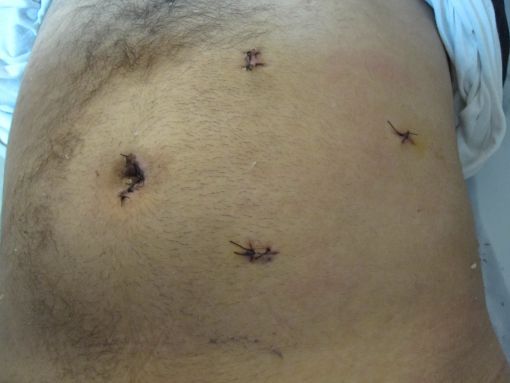
In addition, in laparoscopic surgeries, apart from the incision made for the operation, wide muscle cuts are not made as in open surgeries, which results in less pain. The recovery time to return to normal life is also quite short. Below is a picture of another patient after the surgery.
Laparoscopic urological surgeries that can be performed include:
- Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy
- Laparoscopic radical cystectomy
- Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy
- Laparoscopic radical nephroureterectomy
- Laparoscopic simple nephrectomy
- Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy
- Laparoscopic ureteroneocystostomy
- Laparoscopic Burch and other suspensions
Most urological surgeries are successfully performed with laparoscopic and robotic surgical techniques in our center.